What is an Electrical Cable? A Comprehensive Guide
Electrical cables form the foundational infrastructure of modern society, enabling the safe and efficient transmission of electric power and signals across vast distances and diverse environments. As of November 2025, these engineered assemblies continue to evolve with advancements in materials and design, supporting everything from household appliances to global power grids. This article provides a professional overview of electrical cables, exploring their definition, components, types, operational principles, applications, and safety considerations.
Table of Contents
1. Definition and Historical Development
An electrical cable is an assembly of one or more insulated conductors enclosed in a protective sheath, designed to transmit electrical energy or telecommunication signals. Unlike single wires, cables incorporate layered protection to withstand mechanical stress, environmental conditions, and electromagnetic interference.
The concept dates back to the early 19th century with the advent of telegraphy, where insulated wires were bundled for underwater and underground use. The development of vulcanized rubber by Charles Goodyear in the 1840s and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) in the 20th century revolutionized cable insulation, paving the way for modern power distribution systems.
2. Key Components of Electrical Cables
Electrical cables consist of several layered elements, each serving a specific function to ensure reliability and safety. The following table outlines the primary components:
| Component | Description | Primary Materials | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conductors | Core elements carrying electric current; solid or stranded. | Copper, aluminum | Provide low-resistance pathway; stranded for flexibility. |
| Insulation | Dielectric layer surrounding conductors. | PVC, XLPE, rubber | Prevents leakage and short circuits; resists heat and moisture. |
| Shielding | Optional metallic layer for interference protection. | Aluminum foil, copper braid | Minimizes electromagnetic interference. |
| Armor | Mechanical protection for harsh environments. | Steel wire/tape | Guards against physical damage. |
| Outer Jacket | External protective covering. | PVC, LSZH, polyurethane | Shields from abrasion, chemicals, and fire. |

Figure 1: Labeled cross-section illustrating basic cable components
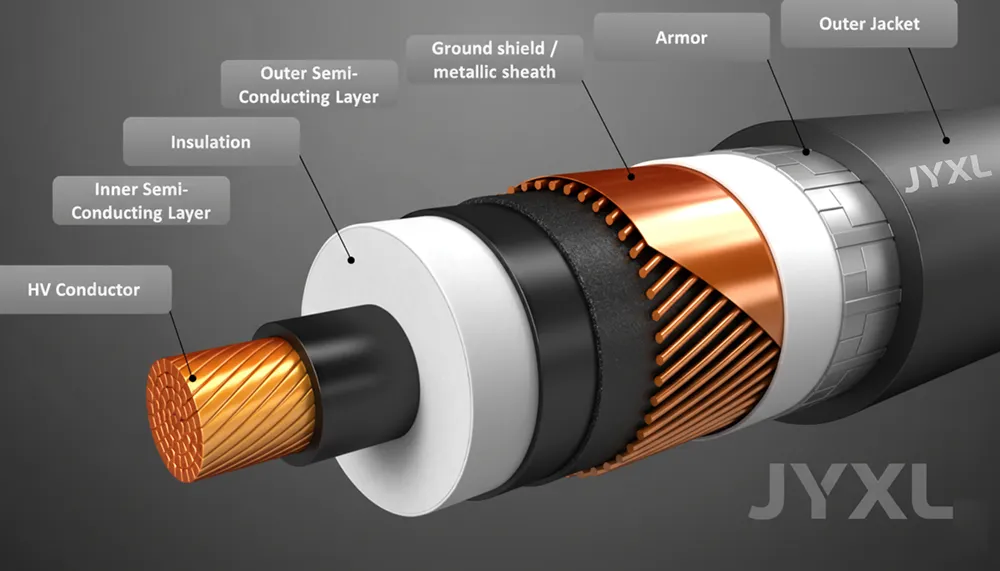
Figure 2: Advanced layered construction in a medium-voltage power cable
3. Common Types of Electrical Cables
Electrical cables are classified by application and construction. Principal types include:
- Power Cables: For energy transmission (e.g., NM-B for residential, armored for industrial).
- Communication Cables: For data signals (e.g., coaxial, twisted pair, fiber optic).
- Shielded Cables: With EMI protection for sensitive electronics.
- Armored Cables: Featuring metal reinforcement for underground or exposed installations.
- Specialized Cables: Including submarine, high-temperature, or low-voltage control cables.
4. How Electrical Cables Work
Electrical cables operate on principles of electromagnetism, where conductors carry alternating or direct current while insulation maintains electrical separation. Shielding employs Faraday cage effects to block interference, and armor provides structural integrity under stress.
5. Applications in Daily Life and Industry
From household wiring and telecommunications to renewable energy grids and electric vehicles, cables enable reliable power delivery. In industry, high-voltage cables support substations, while submarine cables facilitate international data transfer.
6. Safety Considerations and Standards
Proper selection prevents hazards like overheating or shocks. Compliance with standards such as IEC, NEC, or UL ensures performance. Key practices include correct sizing, grounding, and environmental matching.
7. Future Trends
Advancements focus on superconducting materials, enhanced sustainability (e.g., halogen-free jackets), and smart cables with integrated sensors for real-time monitoring.
8. Conclusion
Electrical cables represent a critical yet often overlooked technology underpinning modern civilization. Understanding their design and application fosters safer, more efficient electrical systems. For specific projects, consultation with qualified professionals is recommended.
Comments
Post a Comment